This is Letizia Filippi and the gossip is that she is the new woman in the life of footballer (soccer) Cristiano Ronaldo. The claims are unsubstantiated as other talk is that his relationship with Nereida Gallardo isn't completely over, at least not as far as she is concerned. Letizia has admitted that she has had dinner with Ronaldo and her agent says the couple are 'very, very good friends'. But he would say that - it's good publicity whether true or untrue.
Letizia has admitted that she has had dinner with Ronaldo and her agent says the couple are 'very, very good friends'. But he would say that - it's good publicity whether true or untrue.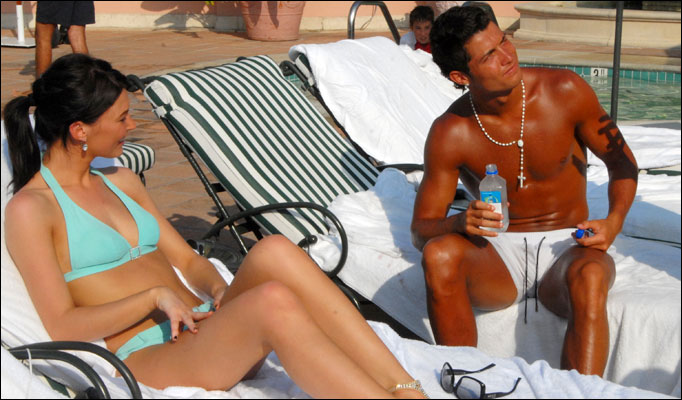 The Italian Letizia Filippi is well known in Spain, lives in Rome and one of her claims to fame is that she finished third in the 1994 Miss. Italy. She is 30 years of age and has had liaisons with numerous well known sportsmen over the years.
The Italian Letizia Filippi is well known in Spain, lives in Rome and one of her claims to fame is that she finished third in the 1994 Miss. Italy. She is 30 years of age and has had liaisons with numerous well known sportsmen over the years.
“….geographers, in Afric maps, With savage pictures fill their graps, And o’er unhabitable downs Place elephans for want of towns.”
These word were written by Jonathan Swift, the author of Gulliver’s Travels. He wrote them more than 200 years ago. Swift was pointing out how little the Europeans of his day knew about Africa. It was a “dark continent” to them – huge and vast and un known. It remained so for centuries.
Africa is the world’s second largest continent. Only Asia is larger. Africa is larger enough to hold nearly four continents the size of Australia. The giant continent straddles the equator, stretching both north and south about 35 degrees. But because of Africa’s shape, the bulk of its land lies beetwen the Tropic of cancer and the Tropic of Capicorn. This means that most of Africa is in the tropics. Indeed, Africa is the most tropical of the continent.
The giant continent straddles the equator, stretching both north and south about 35 degrees. But because of Africa’s shape, the bulk of its land lies beetwen the Tropic of cancer and the Tropic of Capicorn. This means that most of Africa is in the tropics. Indeed, Africa is the most tropical of the continent.
Every time you turn on oyur radio or listen to television or a juke box, these is a good chance that the music you hear will be at least partly African in origin. This is because the music of Europe and America. It began when black Africans were transportedto America as slaves, taking their songs and dances with them. Gradually, as they became accustomed to their new home, they combined their own music with the folk music and Amreican Indian music they heard in the New World. The result was a new and original American folk music. Largely out of this grew jazz, one of the most popular forms of music today. African music is considered primitive because it comes from people who do not have a written language; song are passed on by word of mouth rather than by the use of written notes. Yet it does not seem right to call this music primitive, since some of it is more highly developed than the folk music of Europe and America
African music is considered primitive because it comes from people who do not have a written language; song are passed on by word of mouth rather than by the use of written notes. Yet it does not seem right to call this music primitive, since some of it is more highly developed than the folk music of Europe and America
 So, you’ve bought a new guitar! If you are like I was, you’ve been going to barbeques for years, having a couple of beers and watching your mates sitting around with their guitars, playing songs you’ve known for years and would love to play! So you finally spent the money and bought a guitar – now what?
So, you’ve bought a new guitar! If you are like I was, you’ve been going to barbeques for years, having a couple of beers and watching your mates sitting around with their guitars, playing songs you’ve known for years and would love to play! So you finally spent the money and bought a guitar – now what?
You want to learn fast – so you can join in. For this article, I’m going to assume that you’re a beginner who wants basic proficiency.
I’ve done some research on this, as it was where I was, and I found a connection between people who want to “play fast” and those who already play but just want to play "faster". The connection is quite simple, yet very profound.
Through what I found out, I believe there are two parallels:
1. Study the techniques involved which will make your overall playing faster, and
2. Re-focus your practice sessions onto the basic concepts that beginners learn, which will allow you to become a faster player.
There is a useful acronym that you can use to help focus your practice and improve your playing: M.O.S.T.
M for Memorization
You can have the world's best "ear", but if you don't memorise:
a) the fretboard notes and
b) the major and minor key chords and scales,
it won't matter how good your ear is. The most frustrating thing about learning a new song is finding that chord or note that you know you've learned but just can't remember! It's funny that song writers don't give you time in the middle of their pieces to find that Aminor chord, or work out if a Db minor chord works in a song in B, and then if it does, where it is on the fretboard!
If you are a beginner - LEARN THE FRETBOARD and memorise it!
If you are more advanced - LEARN THE FRETBOARD and memorise it! You might think you already know it, but can you jump from one note or chord to any other instantly without thinking about it?
O for Observation
Human beings work best when all of the senses work in unison. Try plugging your ears with cotton wool and then trying to play a song. Not very good are you. (People like Ray Charles and Beethoven amaze me).
Your senses of sight, sound and touch all interweave to play guitar. When you play a song really well, you can even taste the applause (just kidding). The more you play, the more your fingers put themselves in the right places, your muscles retain a memory of those positions. You begin to see patterns and relationships on the fretboard. You hear yourself play the correct notes and chords and that gives you confidence, which is essential in fast playing.
Memorization is the foundation for observation, and observation is the key to training your mind and hands to work in concert automatically.
S for strength and T for training
This is not weight training! It is really dexterity training (but MODT isn't a word!). However, being dextrous means you have strength in your fingers in order to play the chords you need to play when you need to play them.
Beginners often struggle to hold down chords and play scales with all four fingers. Consistent and correct practice is the only way to build strength, muscle memory and finger dexterity.
The same problem occurs for intermediate players - the most likely culprit for slow play is a deficiency in strength, dexterity and/or correct technique.
Practise your finger exercise and chord making perfectly - don't settle for "that'll do" or "near enough". You want to train your fingers to go to the correct place in the correct way every time! Sloppy exercises will not help.
In conclusion, the key to learning guitar faster - as well as playing it faster - rests in following the M.O.S.T. formula. It really is all about getting the basics right from the start!
About The Author
Greg Millican
http://www.strumandpick.com
For free advice, lessons and downloads on guitar for beginners and intermediate players.
Introduction
3GP or .3gp is the third generation video standard. It integrates mp3, mp4, 3gpp, 3g3p and 3g2.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia (See Wikipedia)3GP is a multimedia container format defined by 3GPP for use on 3G mobile phones. It is a simplified version of MPEG-4 Part 14 (MP4). 3GP files have the filename extension .3gp or .3g2.
3GP stores video streams as MPEG-4 or H.263, and audio streams as AMR-NB or AAC-LC formats. 3GP files are always big-endian. 3GP also describes image sizes and bandwidth, so content is correctly sized for mobile display screens.
3GP files are viewable on a PC using QuickTime or RealPlayer.
MPEG-4 Part 14, formally, ISO/IEC 14496-14:2003, is a multimedia container format standard specified as a part of MPEG-4. It is most-commonly used to store digital audio and digital video streams, especially those defined by MPEG, but also can be used to store other data such as subtitles and still images. Like most modern container formats, MPEG-4 Part 14 allows streaming over the Internet. The official filename extension for MPEG-4 Part 14 files is .mp4, thus the container format is often refered to simply as MP4.
3GPP
The 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) is a collaboration agreement that was established in December 1998. It's a co-operation between ETSI (Europe), ARIB/TTC (Japan), CCSA (China), ATIS (North America) and TTA (South Korea).
Some of the well well-known participants of the 3GPP project are 3, Alvatel Apple, AT&T, BenQ, BT Group, China Mobile Com, Congular Wireless, Cisco, Ericsson, France Telecom, Fraunhofer, Fujitsu, HP, HuaWei, IBM, Intel, KDDI, KPN, LG, Lucent, Microsoft, Mitsubishi, Motorola, NEC, Nippon Ericsson, Nokia, Nortel, NTT DoCoMo, 02, Oki, Panasonic, Philips, Qualcomm, Samsung, Sharp, Siemens, Sony Ericsson, Sun, Swisscom, Tata Consultancy Services, Texas Instruments, Thomson, T-Mobile, TNO, Toshiba, VIA Technologies , Vodafone and Yokogawa, to name but a few.
The scope of 3GPP is to make a globally applicable third generation (3G) mobile phone system specification within the scope of the ITU's IMT-2000 project. 3GPP specifications are based on evolved GSM specifications, now generally known as the UMTS system.
Note that 3GPP should not be confused with 3GPP2, which specifies standards for another 3G technology based on IS-95 (CDMA), commonly known as CDMA2000
Standards
3GPP standards are structured as Releases. Discussion of 3GPP thus freqently refers to the functionality in one release or another.
- Release 98 and earlier releases specify pre-3G GSM networks.
- Release 99 specify the first UMTS 3G networks, incorporating a CDMA air interface.
- Release 4 - originally Release 2000 - adds features including an All IP Core Network.
- Release 5 introduces IMS and HSDPA.
- Release 6 integrates operation with Wireless LAN networks and adds HSUPA.
- Release 7 and onwards are still in the early stages, and work towards better integration with wired networks.
Current 3GPP standards incorporate the latest revision of the GSM standards. 3GPP documents are made available freely on the organisation's web site. Whilst 3GPP standards can be bewildering to the newcomer, they are a remarkably complete and detailed resource and provide insight into how the cellular industry works. They cover not only the radio part ("Air Interface") and Core Network, but also billing information and speech coding down to source code level. Cryptographic aspects (authentication, confidentiality) are also freely specified in detail. 3GPP2 offer similar information about their system.
Deployment
3GPP systems are deployed across much of the established GSM market (primarily Release 99 systems to date). As of 2005, 3GPP systems are seeing deployment in the same markets as 3GPP2 systems (for example, North America). Industry commentators speculate constantly about the competing systems, with the outcome far from clear.
3GPP specification
The term "3GPP specification" covers all GSM (including GPRS and EDGE) and W-CDMA specifications. The following terms are also used to describe networks using the 3G specifications: UTRAN, UMTS (in Europe) and FOMA (in Japan). Revised versions of many of these specifications are produced up to four times a year following the quarterly TSG plenary meetings. (TSG GERAN meets five times a year.) See the table below which gives links to lists of specifications arising from each plenary TSG meeting since the freezing of Release 1999. The month of the meeting and the meeting number are shown in each case. Note that the tables show only those specifications newly approved or modified at the meeting concerned; they do not contain a complete list of all specifications current following the meeting. For such a list, consult the "status list" - see below.
Following each TSG SA plenary meeting, a complete set of specifications is produced. This set includes not only the new specifications generated at that meeting, but also the latest versions of each specification that was not changed at that meeting. i.e. each directory holds a complete set of specifications. Each set has an associated status list as detailed in the table below. Each set (and corresponding status list) includes the specs arising from the TSG GERAN meetings held since the preceding SA meeting. (GERAN meets asynchronously from the other TSGs.)
The Status List (ZIPped RTF or Word format) summarizes the current version number for every release of every 3GPP specification following each TSG plenary meeting. Also listed for each specifications are:
- the 3GPP working group and rapporteur responsible for the specification
- the Project Manager in MCC (Mobile Competence Centre) responsible for the specification
- the meeting at which it was, or is expected to be, "frozen" (i.e. the point after which only corrections are allowed)